reviewed by Christina Lopez
A plant is either Monocotyledon or a Dicotyledon. The two vary in their structural attributes: roots, stems, leaves, and the flower. The variation begins from the very start of a plant's life cycle. Initially, the seed of a plant helps us discover if it's either a Monocot or a Dicot Plant.
The angiosperms or otherwise known as the flowering plants are incredibly diverse. To simplify things, we divide them into two main types, which help us understand the nature of these plants and guides to what they require.

The Cotyledon refers to the first leaf present within the embryo. If a single leaf is present, it will be classified as a Mono, and if two leaves exist, then a dicotyledon. The small difference between the two seeds increases as the plant grows. When a plant first starts to extend its roots, the variation between seeds starts to become visible.
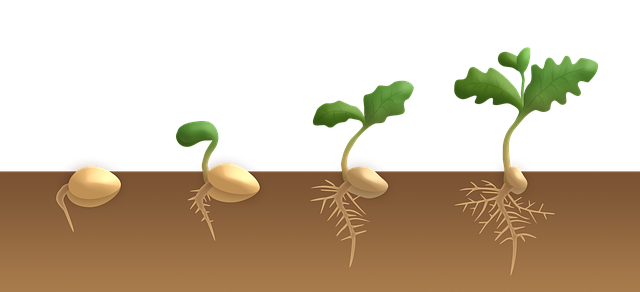
The monocots tend to have fibrous roots, while the dicots establish a tap root system.
When the leaves on the stem appear, the former shows parallel venation, while the latter has numerous auxiliary veins with reticulate or net venation. Finally, if the flower petals are multiple or equal to three, they are grouped as a monocot. If the petals are four-five or divisible by them, then indeed categorized as dicots.
Contents

The large white flower with three petals has two sets of three leaves.

The sunny yellow flower blooms in springs. The monocot flower is famous for its ability to attract honeybees.
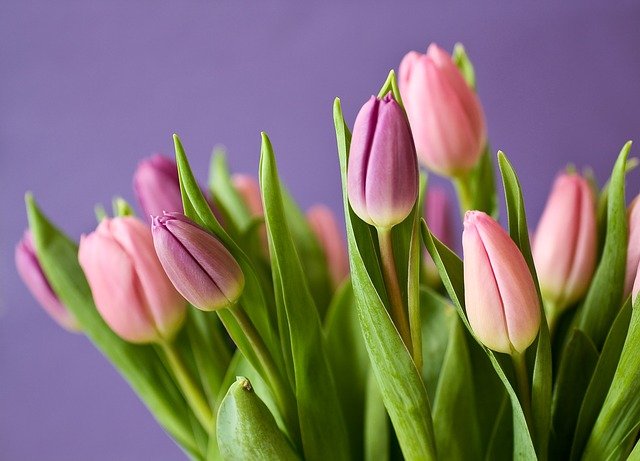

The multiple layers of petals in a tulip bulb makes it difficult to count the petals, but the vivid plant is classified as a monocot.

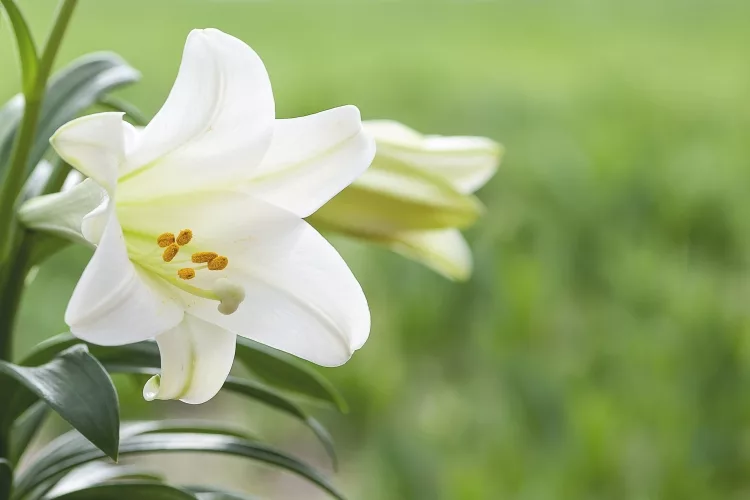
Lilies are considered one of the most beautiful flowers, and rightly so. Although the colour of the flower varies, it usually has six or more petals.
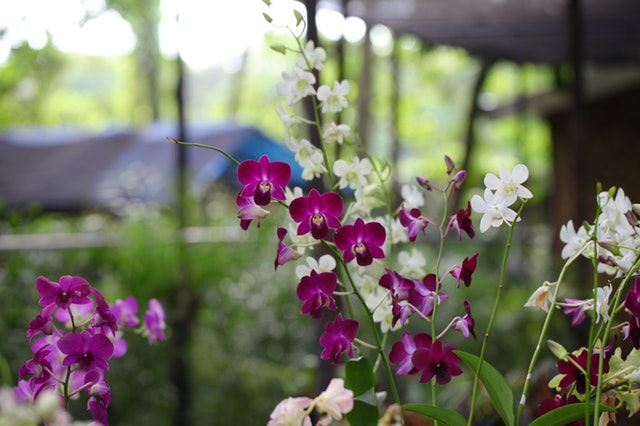

The orchids are the most common species of flowering plant.it is adaptable to all kinds of temperatures.
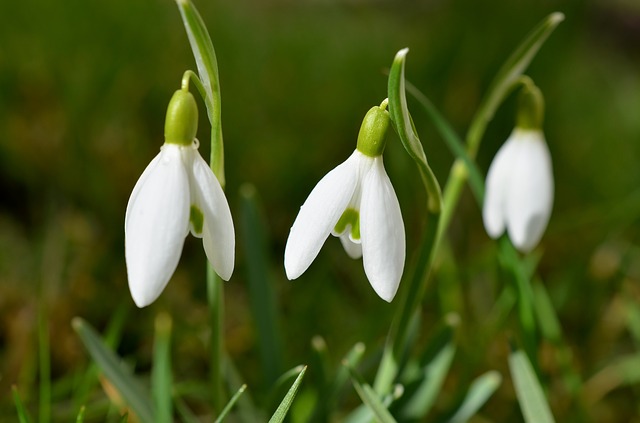

The flower appears small and white, just as the name suggests.
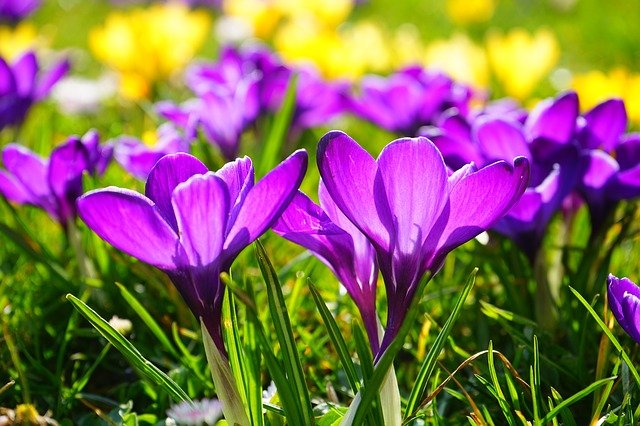

The autumn-bloomer Crocus is a magnificent lilac flower that blooms until the winter arrives.
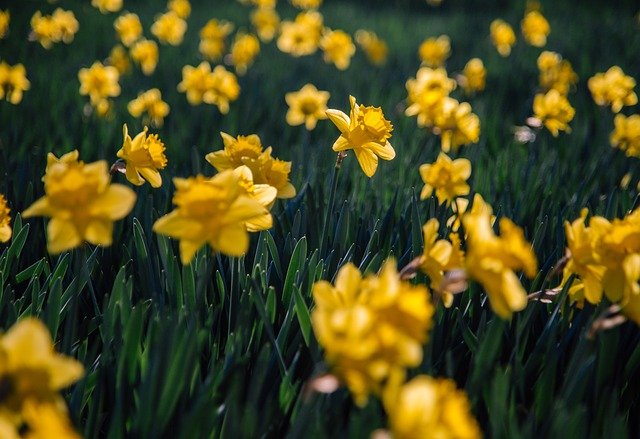

The cheerful yellow flower has unusually arranged six petals, which give it a unique shape.
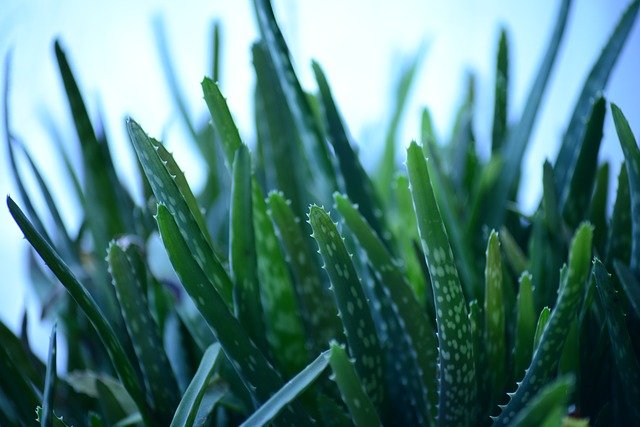

The fleshy leaves of the aloe vera plant are used for its tremendous benefits for health.

The spiky red flowers can be mistaken for red chillies from afar. The contrast between the green leaves and the vibrant flower catches the eye.
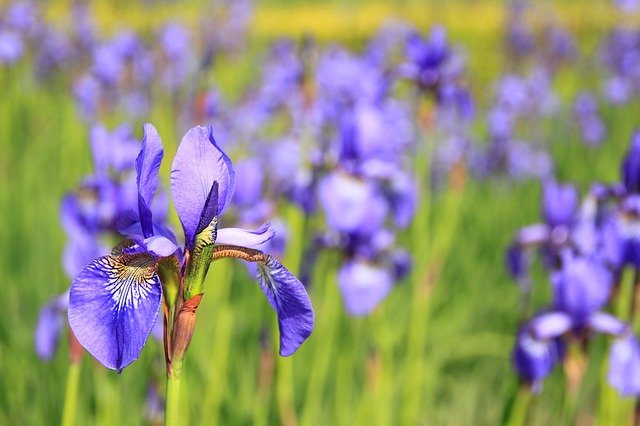

The iris flower has an extensive range of colours, yet all are equally beautiful.
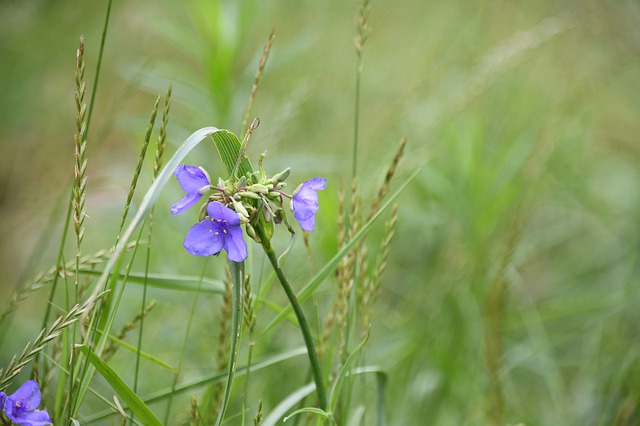

The three-petaled spiderwort flowers are usually blue and purple and are quite resilient.

The ornamental grass is known for the colourful foliage. The green grass turns into orange and bronze during the winters.

Also known as Rubra, the red tussock comes from the grass family.
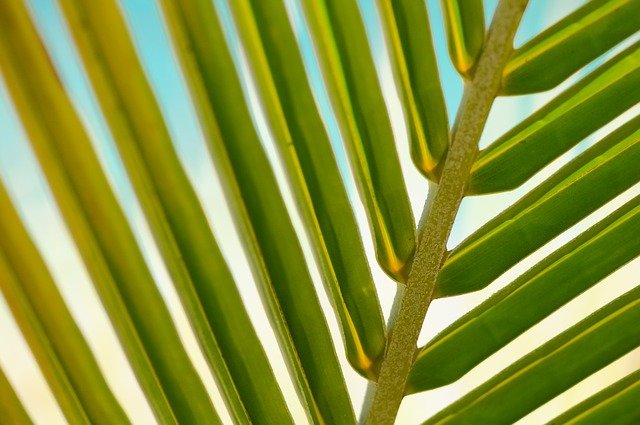

The Arecaceae: commonly known as the palms are stemless monocot plants that can grow as shrubs, climbers, and trees.

From the Poaceae family, bamboo is a widespread species with numerous uses. The unique structure of the plant distinguishes it from the rest.

The banana tree is a popular monocot fruit free from the tropics, with enormous leaves.

Sweet pineapple is found in tropical areas and is native to South America.
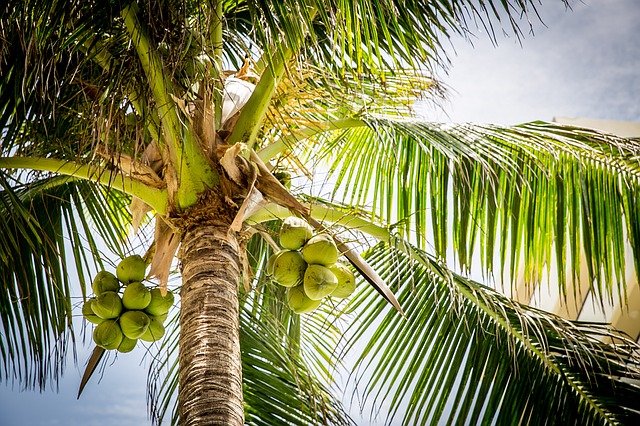

Woody hard coconuts are the seeds of tropical palms.
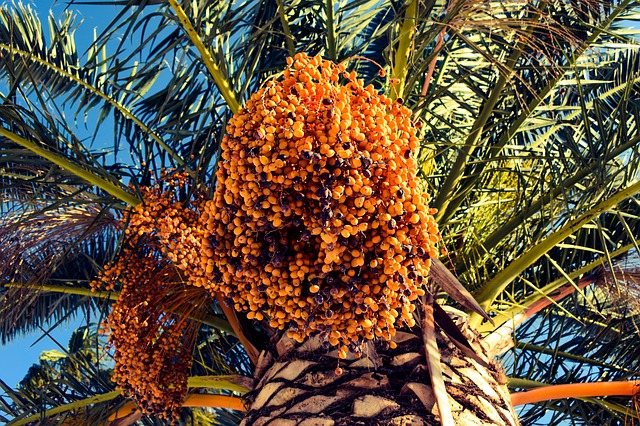

The date palms produce the sweet fruit.
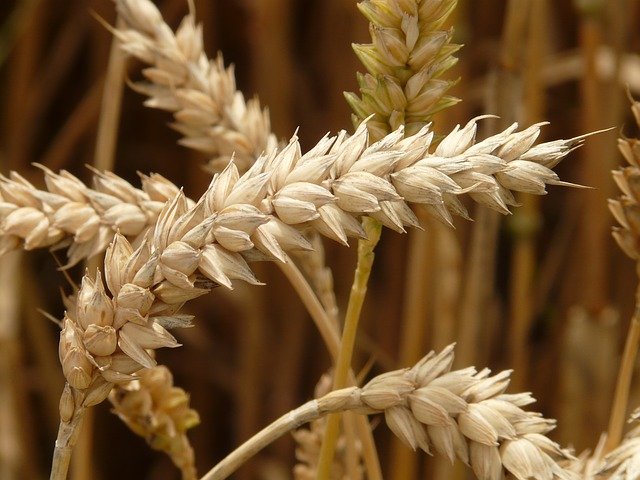

A vital crop, processed to be used in the form of flour in our daily meals.
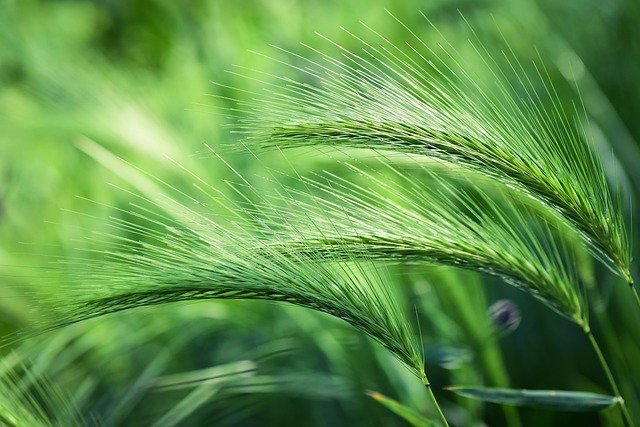

A prominent cereal grain harvested in large amounts can be a healthy part of the diet.
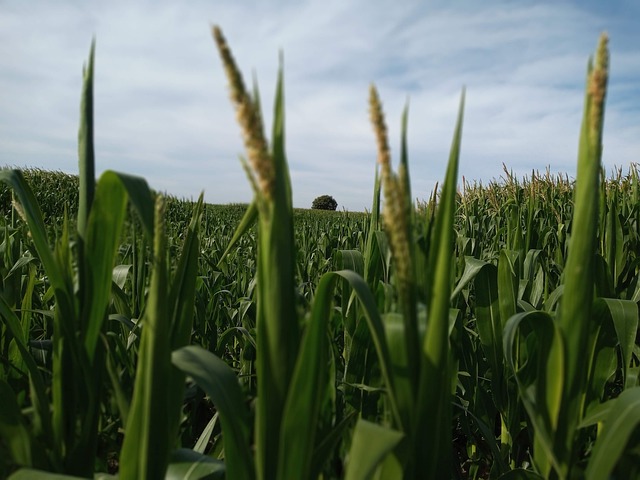

Also known as corn. The maize crop important grain used for making several goods.

Commonly used in the kitchen, the garlic plant can be grown in a kitchen garden as well.
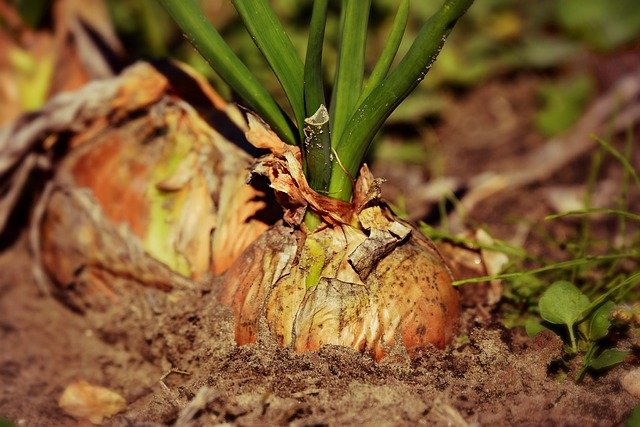

Widely cultivated vegetable, commonly used in meals

The colossal oak trees are a source of food and shelter for birds.
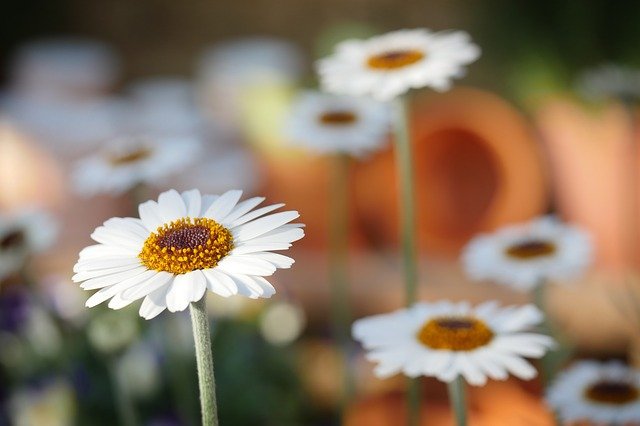

The white and yellow daisy flower is an absolute beauty.
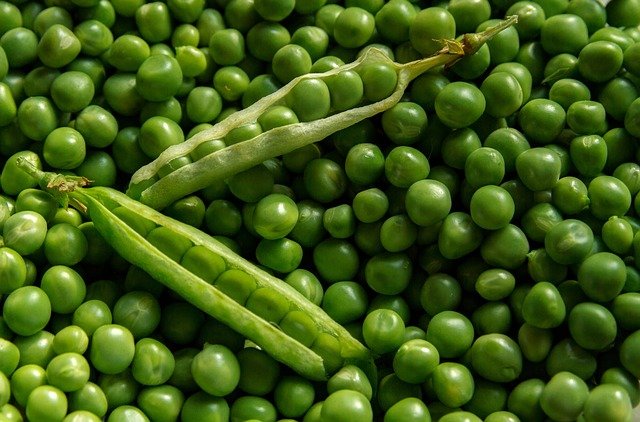

The small spherical peas are used as a vegetable.


The ornamental desert plant is one of its kind.
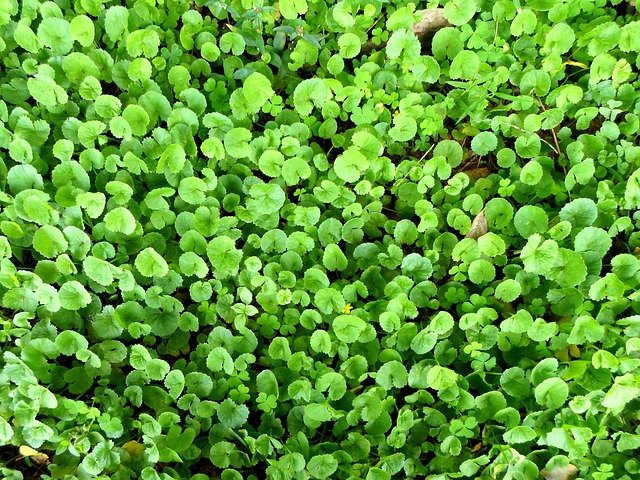

Indian pennywort is a herbaceous and perennial plant that is often used as a culinary vegetable.
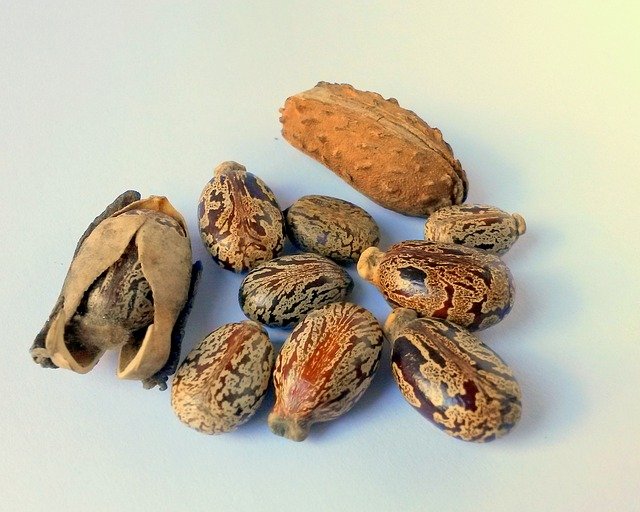

It is a perennial flowering plant. It is mostly consumed, mostly in the form of oil.
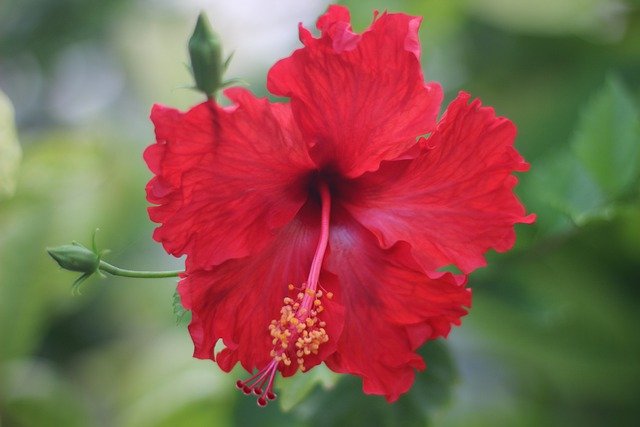

The ornamental plant is grown throughout the tropics; it is slightly fragrant and mostly crimson.
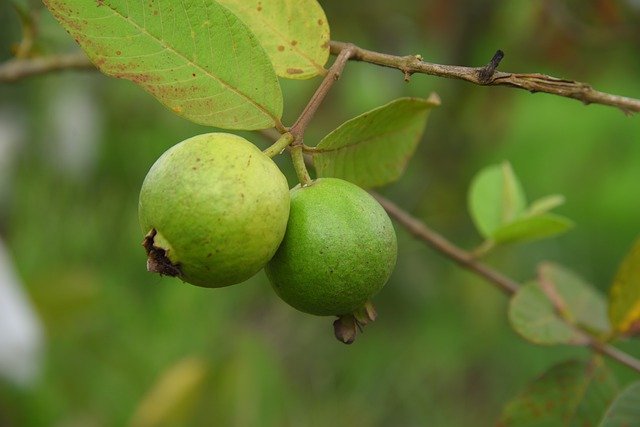

Tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical regions is sweet and soft to eat.

It is known as the king of fruits; the sweetest fruit has no alternate.
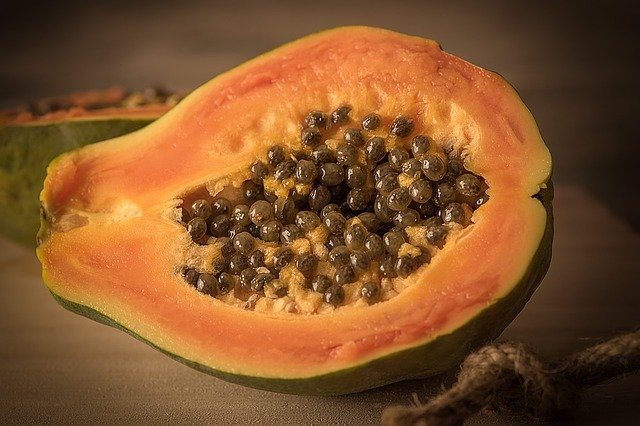

Grown in the tropical regions and is characterized for its shape and colour
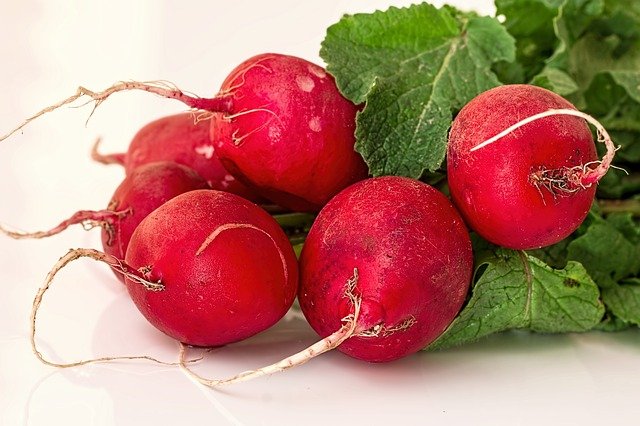

An edible root vegetable, consumed throughout the world for a variety of health benefits.

The juicy red tomato can be consumed raw and cooked.
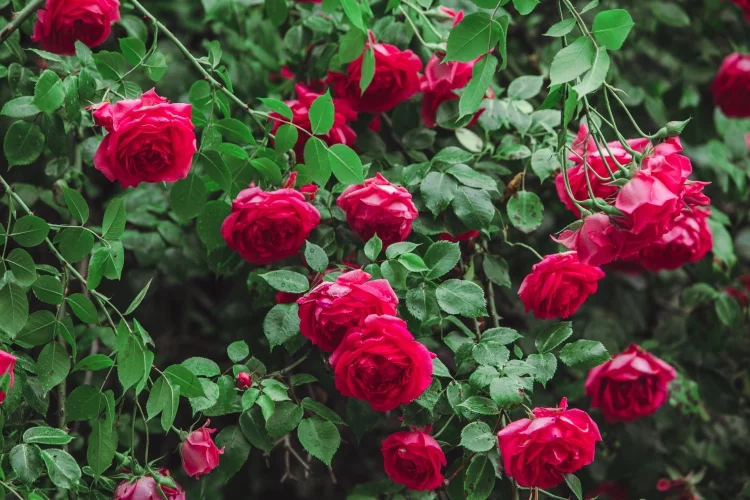

The rose flower needs no description. The shrub is known for the magnificent beauty that blooms.

The summer flower with a wide disc and tough petals is a worldwide famous plant.
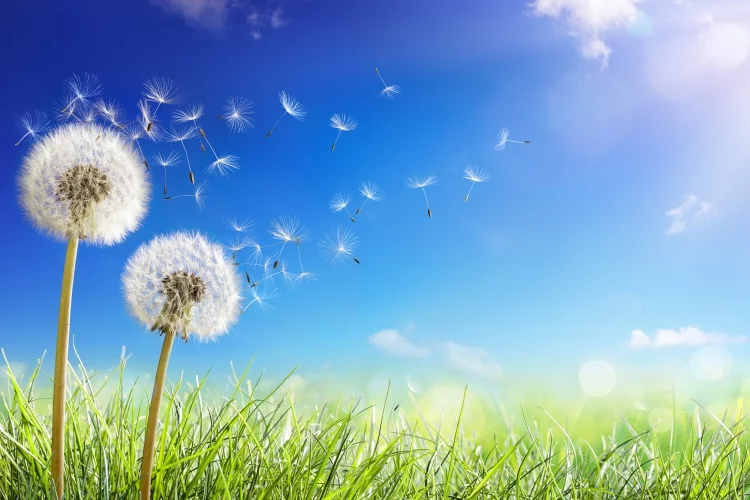

Abundant yellow flowers are also considered as a herb and have medical properties.
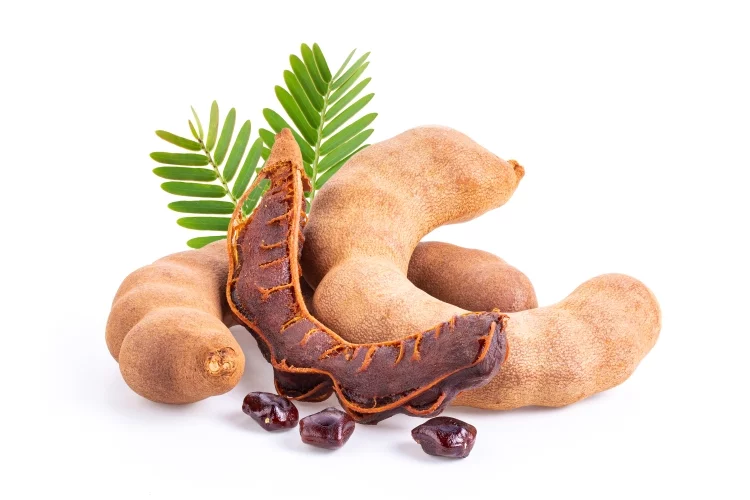

The tree produces bean-like pods filled with seeds surrounded by a fibrous pulp.
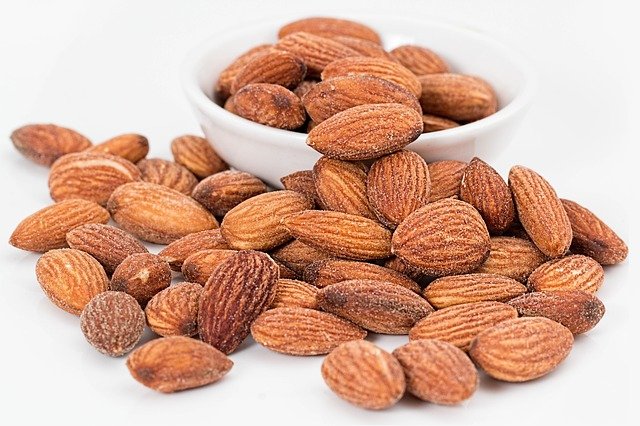

Native to middle-east almond are seeds with tremendous health benefits/
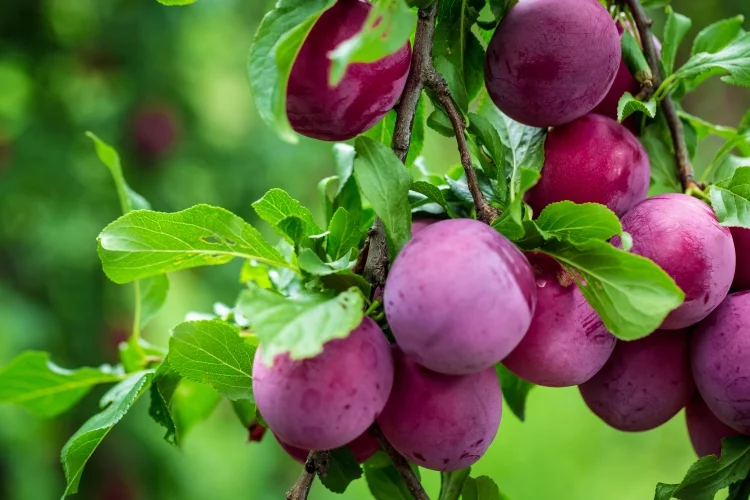

A juicy fruit can be consumed fresh and dry.
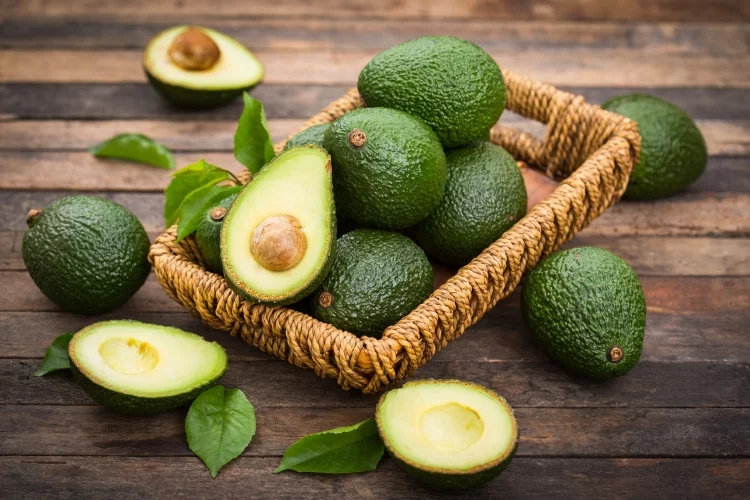

A large berry containing a single large seed contains multiple vitamins.
Small olives are impressively high in nutrients.
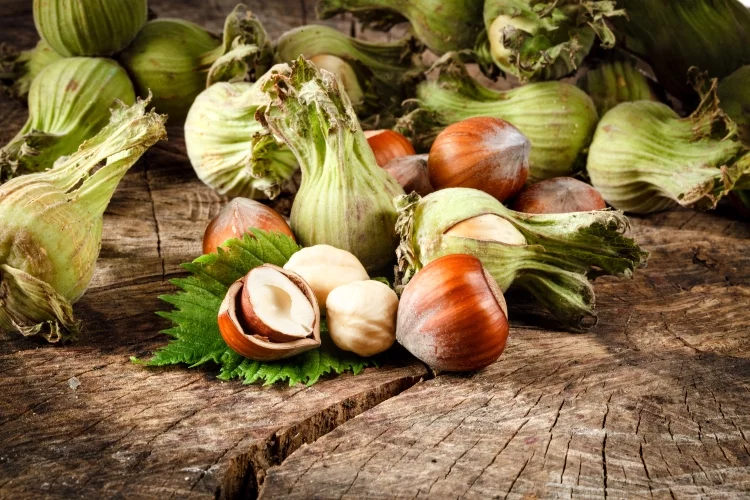

Hazelnuts are loved by people, squirrels, and hazel dormice.
The vivid red poppy has a lot of significance and is used as a symbol of wealth.
Legumes are grown for human consumption and for livestock forage. They are great source of Proteins.
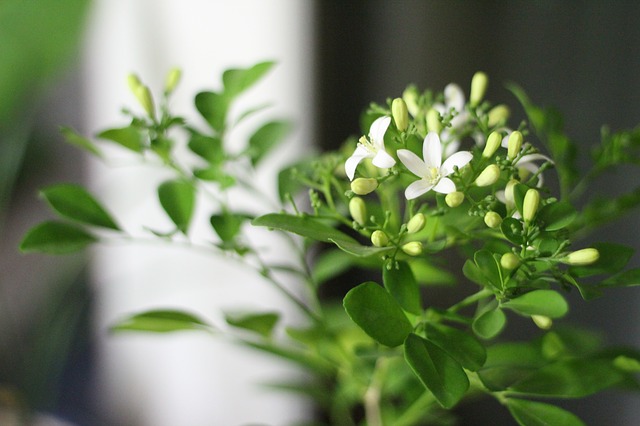

The famous night fragrant white flower is majestic.
Monocots and dicots are two types of flowering plants. Both produce seeds in structures called fruit, although monocots produce one seed per fruit while dicots produce several seeds in each fruit. This article will explain what these terms actually mean, their differences and similarities, and how they relate to other parts of the plant.
The term "monocot" is a much older one than "dicot," and was coined by botanist Adanson in 1763 to describe plants with one seed leaf. These plants tend to be herbaceous, or soft stemmed. They typically have parallel-veined leaves, parallel leaf veins, and often possess flower parts in multiples of three. Monocots include grasses, orchids and palm trees.
Dicots are a much more recent classification system for plants. They were first defined by Linnæus in 1737 as having two seed leaves with net-like venation. Dicots are generally woody plants and include trees, roses, daisies and beans.
Let's looks at three key characteristics that allow you to distinguish between monocots and dicots: the number of seed leaves their flowers produce; the arrangement of their flower parts; and whether they have vascular cambium tissue in their stems.
A monocot produces a single seed leaf, also known as a cotyledon, while a dicot produces two embryonic leaves in the seed that later expand into true leaves once the plant germinates. This embryonic seed leaf is also called a seed leaf.
The number of petals on a flower or the shape of its sepals can help you to determine whether it's a monocot or dicot. As mentioned above, monocots typically have flower parts in multiples of three while dicots tend to have flower parts in multiples of four or five.
On a stem cross-section, if you see a cambium ring, this indicates that the plant is a dicot. Monocots lack vascular cambium tissue and do not show distinct rings on their stems.
Monocots are older than dicots, with most researchers believing they appeared on Earth 60 million years before dicots. Their age may explain why most of the plant kingdom is made up of dicots, although there are still over 10,000 monocot species in the plant world.
A monocot is a plant that typically has one embryonic seed leaf and the vascular bundles in their stems and roots form parallel strands instead of intertwining haphazardly as they do in dicots. Monocots include grasses, lilies, onions, palms, bananas, irises, and orchids.
Dicots (a contraction of the phrase 'two seed leaves') are plants that typically have two embryonic seed leaves and the vascular bundles in their stems and roots form intertwining strands as they do in monocots. Dicots include beans, roses, maple trees, violets, tomato plants, squash, and carrot plants.
It's safe to say that dicots are among the most popular types of flowering plant due to their beauty, variety, and ease of care.
There are different ways you can care for your dicot plants. Generally speaking, how you care for them will vary based on the type of flower they produce. For instance, if you want to grow a rose, you need to make sure it is planted in the right type of soil. You'll also have to water it correctly or else its flowers will wilt and die.
A common mistake when caring for dicots is overwatering them. To avoid this problem, water your plant when the top of the soil is dry, but test it first. You know your plant needs more water if the top layer is crusted or white in color. As you might have guessed, you should allow the soil to dry out before watering it again.
Typically speaking, dicots need an inch of water every week. If you want to maintain healthy flower growth, you should water more on hot days and less when the weather is cool. However, keep in mind that too much water will drown your plant or rot its roots, so it's important to strike a balance.
Another thing to consider when caring for dicots is sunlight. This type of flower needs five hours of direct sunlight per day. When you plant your dicot, make sure to place it in a location where it can get plenty of natural light without getting too much shade.
When caring for dicots, you should also think about their soil. Plants that have a strong root system don't need as much fertilizer as those with weak root systems do because they can absorb nutrients and water more efficiently. This is why it's important to buy a good quality potting soil for your dicot plants.
List of some common monocot plant species and the proper way to maintain them.
Orchid plants are extremely picky and require a lot of care to grow properly. However, there is some good news: they're not hard to maintain! There's only one downside: they require specific elements in order to thrive. If your plants don't receive these necessary elements on a regular basis, they'll get sick and eventually die. In order to prevent this from happening, you have to purchase a specific type of potting medium. Keep in mind that orchids require a lot of humidity so it's important for the soil to be humid as well.
We all know that sago palms are extremely popular, especially in the United States. They don't require too much attention but you have to remember to water them from time to time, mainly during spring and summer.
Bamboo palms are a great choice if you're looking for a hardy plant that requires little care while still being extremely easy to maintain. For example, many people forget to water their plants and this is definitely not the case with the bamboo palm: it needs ample watering, especially during spring and summer. Make sure that you water it regularly every two weeks or so. Furthermore, keep in mind that bamboo palms grow slower than other types of houseplants so don't be discouraged if your plant doesn't grow as quickly.
Agave plants are extremely fashionable at the moment and they're easy to maintain if you follow some basic guidelines: make sure that the location has a lot of light and provide it with enough water (but not too much). Also, we recommend that you also fertilize it every two weeks or so while it's growing season.
Aloe vera is an extremely popular succulent that doesn't require much care. You can water it once or twice a week and make sure to choose a pot with drainage holes because this will prevent the plant from getting rot and other dangerous conditions (e.g., root rot).
20 Fastest Growing Trees for your Garden in India
9 o'clock Flower- Plant Care & Benefits
Rice Water for Plants to Get Maximum Growth
How to Carry Plants on Domestic Flights in India?
10 Examples of Plants that have Fibrous Roots
 |
 |
 |
 |

About Christina Lopez
Christina Lopez grew up in the scenic city of Mountain View, California. For eighteen ascetic years, she refrained from eating meat until she discovered the exquisite delicacy of chicken thighs. Christina is a city finalist competitive pingpong player, an ocean diver, and an ex-pat in England and Japan. Currently, she is a computer science doctoral student. Christina writes late at night; most of her daytime is spent enchanting her magical herb garden.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Get new FREE Gifts. Or latest free growing e-books from our latest works.
Disable Ad block to reveal all the links. Once done, hit a button below
 |
 |
 |
 |